I love the holidays in New York City. There are so many Christmas themed events to go to and decorated homes to visit. One of my favorite tours is at the Met Cloisters for their Christmas themed walking tours that take place from December through early January.
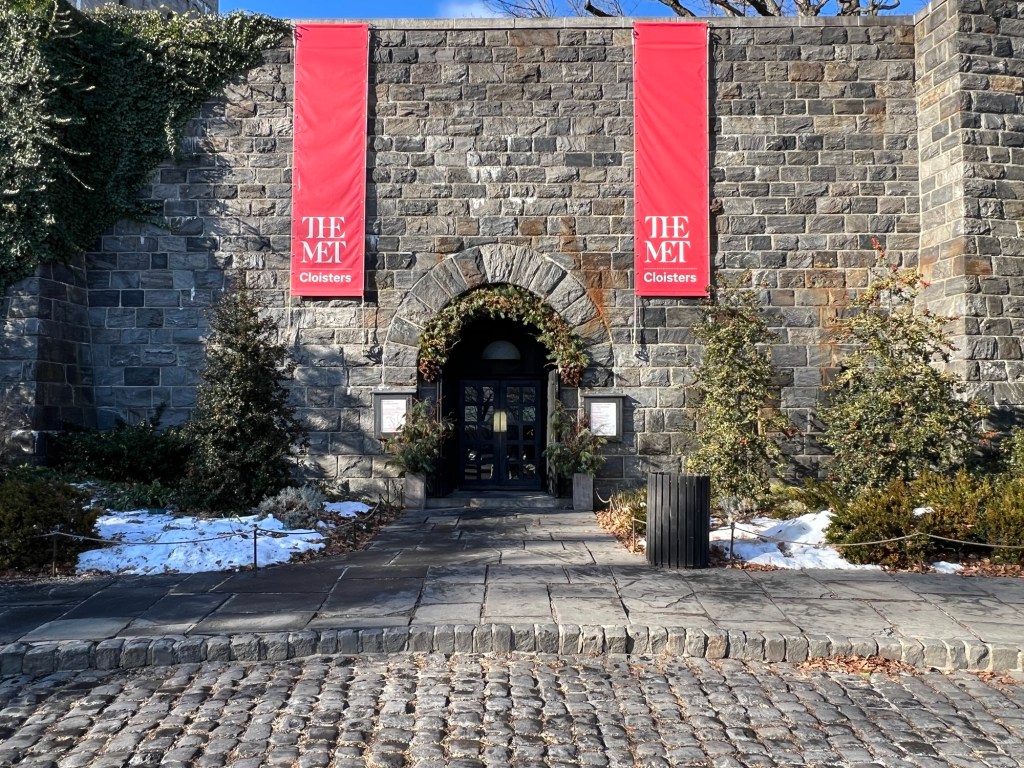

The Cloisters Museum & Gardens: A Branch of The Metropolitan Museum of Art
99 Margaret Corbin Drive
Fort Tryon Park
New York, NY 10040
(212) 923-3700
Open: March-October 10:00am-5:15pm/November-February-10:00am-4:45pm
https://www.metmuseum.org/visit/plan-your-visit/met-cloisters
Fee: Adults $30.00/Seniors $17.00/Children $12.00/Members & Patrons and Children under 12 are free (prices do fluctuate).
Museum Hours:
Hours: Open 7 days a week
March-October 10:00am-5:15pm
November-February 10:00am- 4:45pm
Closed Thanksgiving Day, December 25th and January 1st.
*Some galleries may be closed for construction or maintenance.
TripAdvisor Review:
My review on VisitingaMuseum.com:
To finish my weekend of holiday festivities before the Epiphany, I took the annual Christmas walking tour of the Met Cloisters. The museum hosts an interesting walking tour of the history of the holidays during the Medieval era. Each tour has a different theme to it. There is the history of Christmas in that era, the use of plants and flowers in the decorating of the religious sites and the historic significance of the visit of the Three Kings.
Each tour guide incorporates the artwork, architecture and plants into the discussion. On average you will have about forty people on the tour.
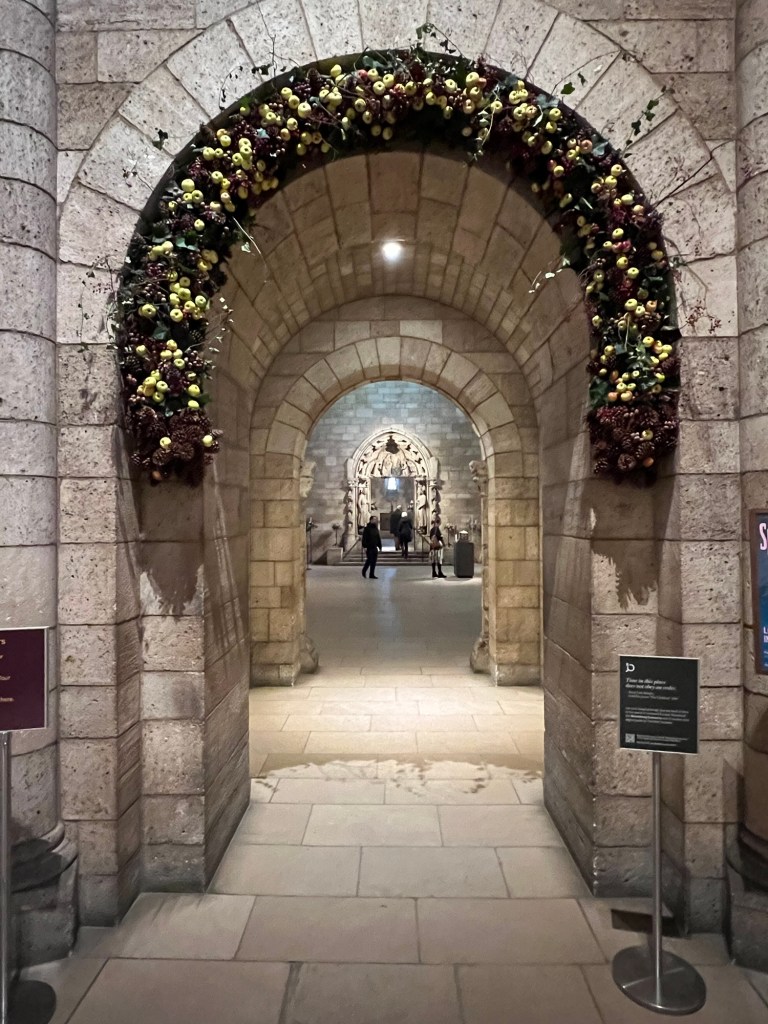

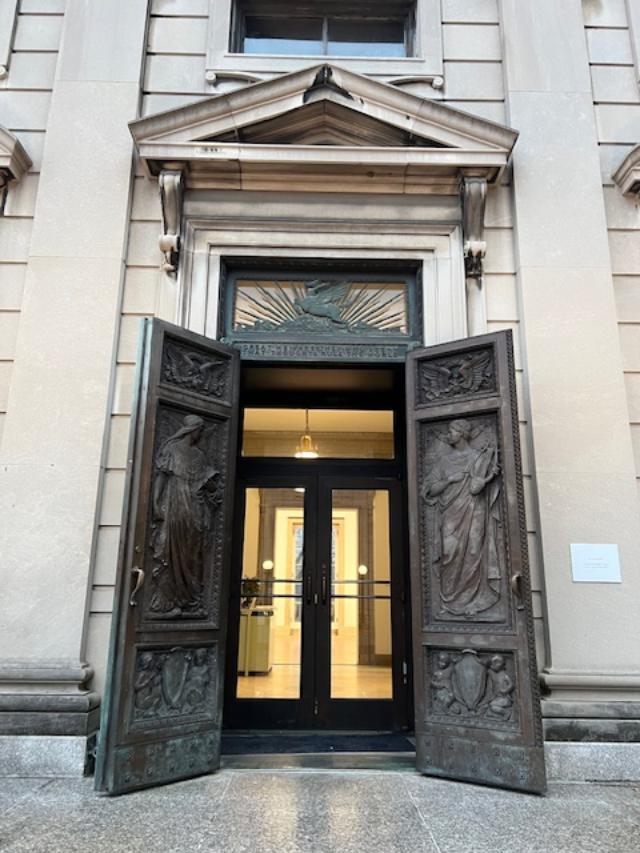
The entrance of the Cloisters decorated for the holidays
The Christmas Tide Tour:
https://www.metmuseum.org/perspectives/christmastide-deck-the-halls
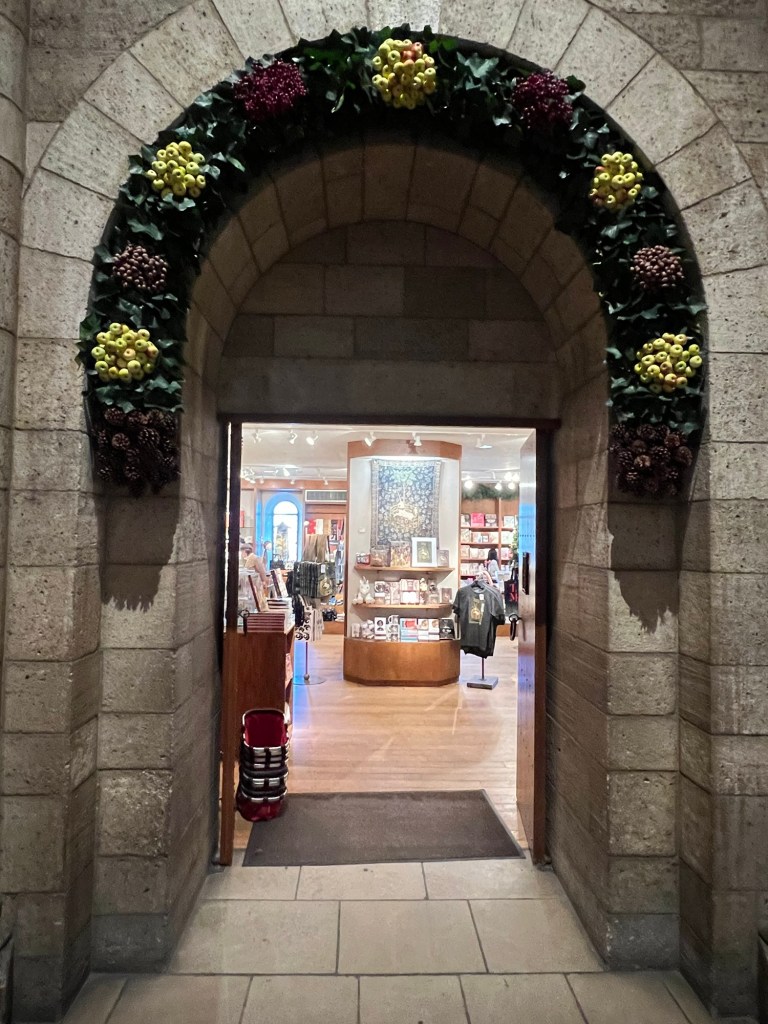

The entrance of the gift shop decorated for the holidays
The archways were decorated with seasonal plants and fruits. I read online that the volunteers went into Fort Tyron Park and collected ivy from the wild to decorate the museum. Every day the museum is open during the holidays these are replaced on a daily basis.
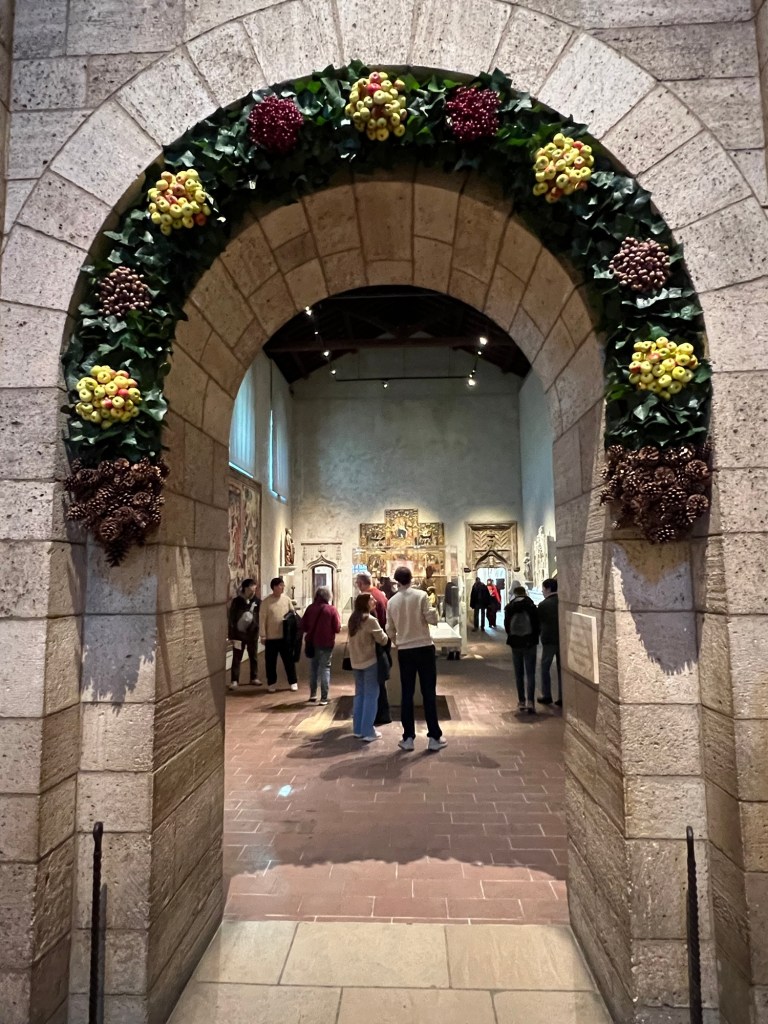

The entrance to the galleries decorated for the holidays
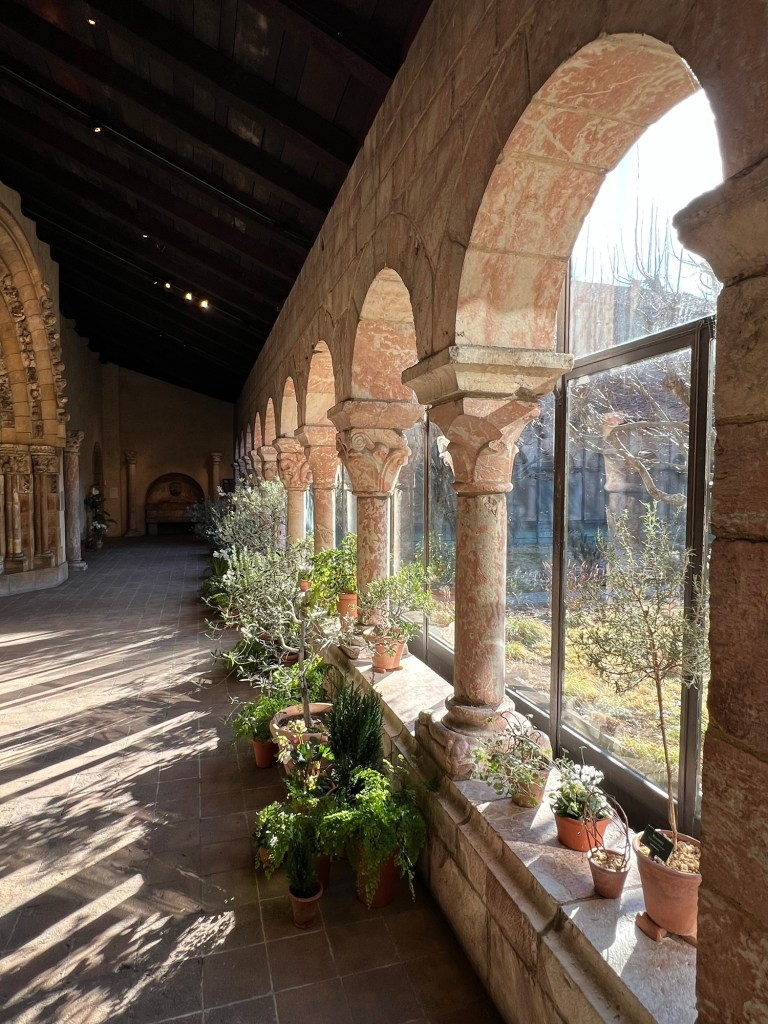

We started the tour with a discussion of plants that once decorated churches and ministries
With the change in attitude towards the Christmas holidays during the Middle Ages and its incorporation into church traditions, decorating for the holidays came back into style. The use of holly, evergreen and mistletoe became part of the Christmas tradition and to justify the decorating, they were related to Christian symbols.
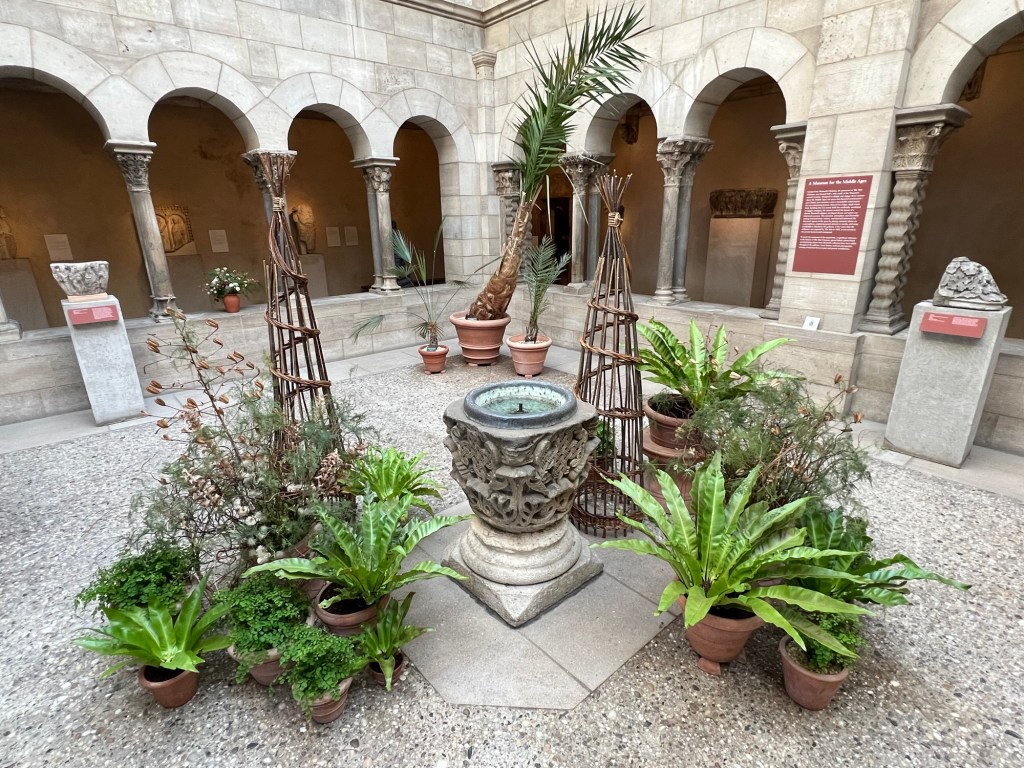

The beauty of the life plants in winter
Each of the Cloisters were lined with fresh greens and potted plants giving each of the Cloisters its own special mood.
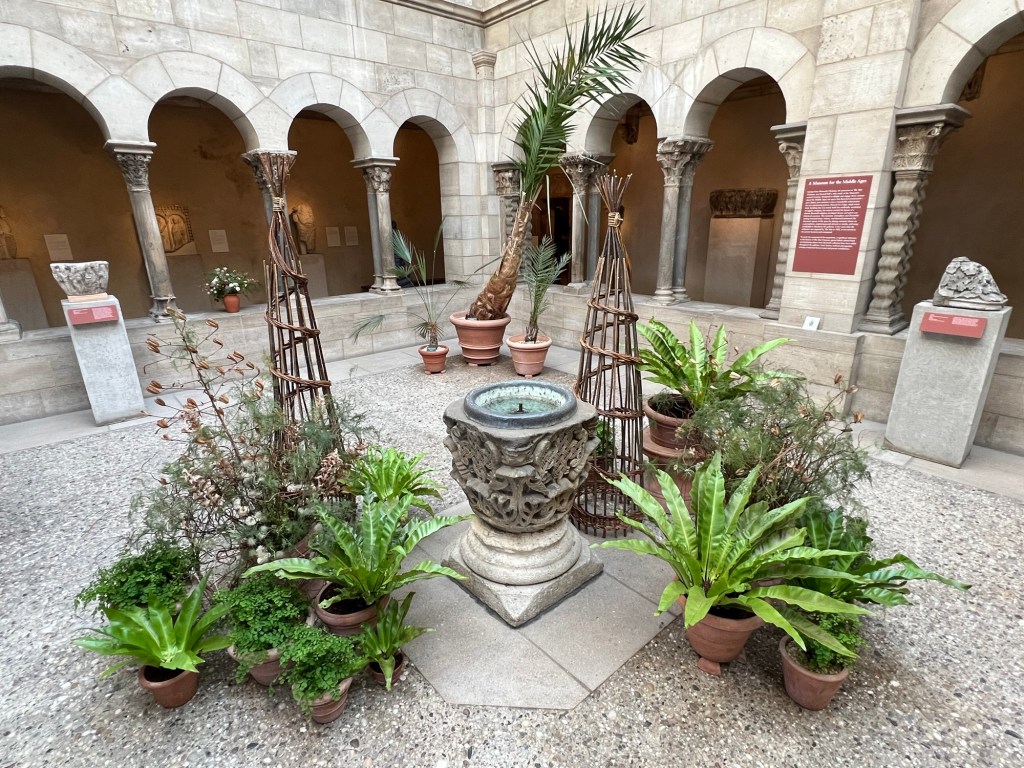

One of the Cloisters bright with plants
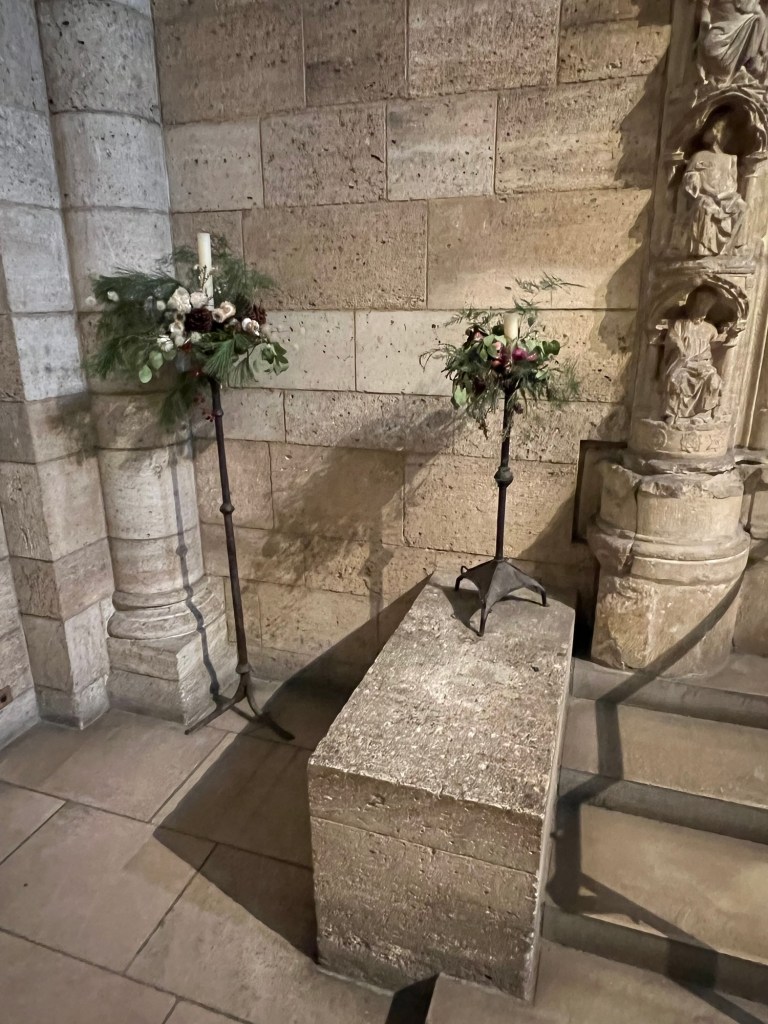

The stairs leading into the chapel decorated for the holidays
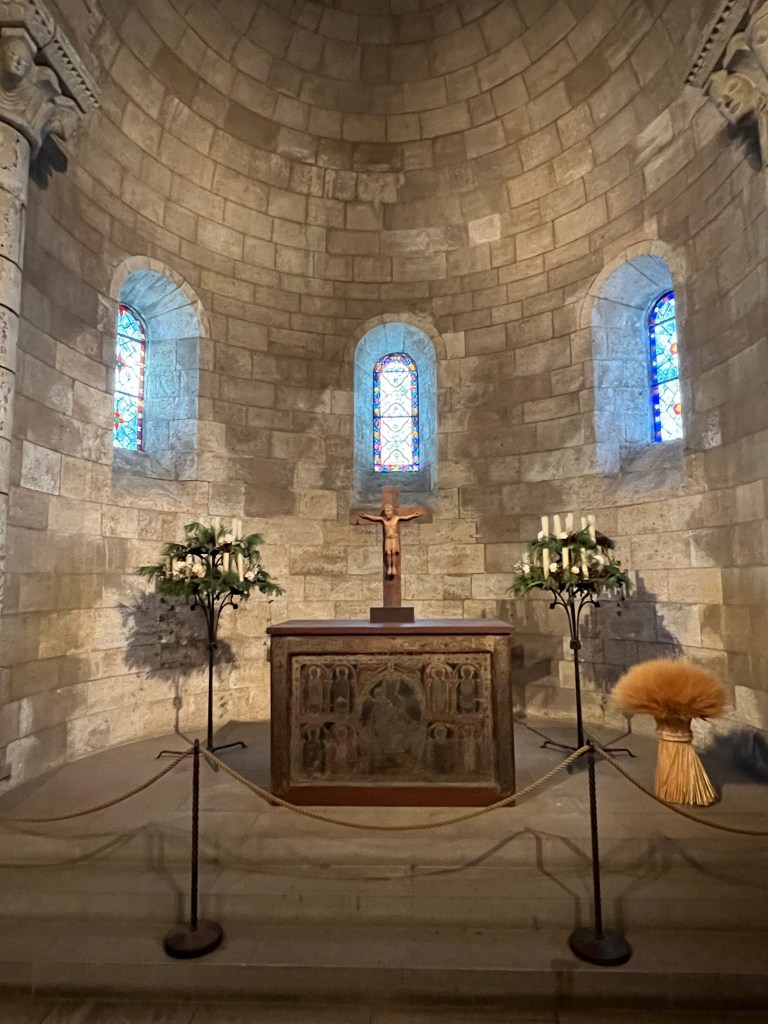

The chapel on the main floor decorated for the holidays

The colorful floral displays lining the window sills of the chapel
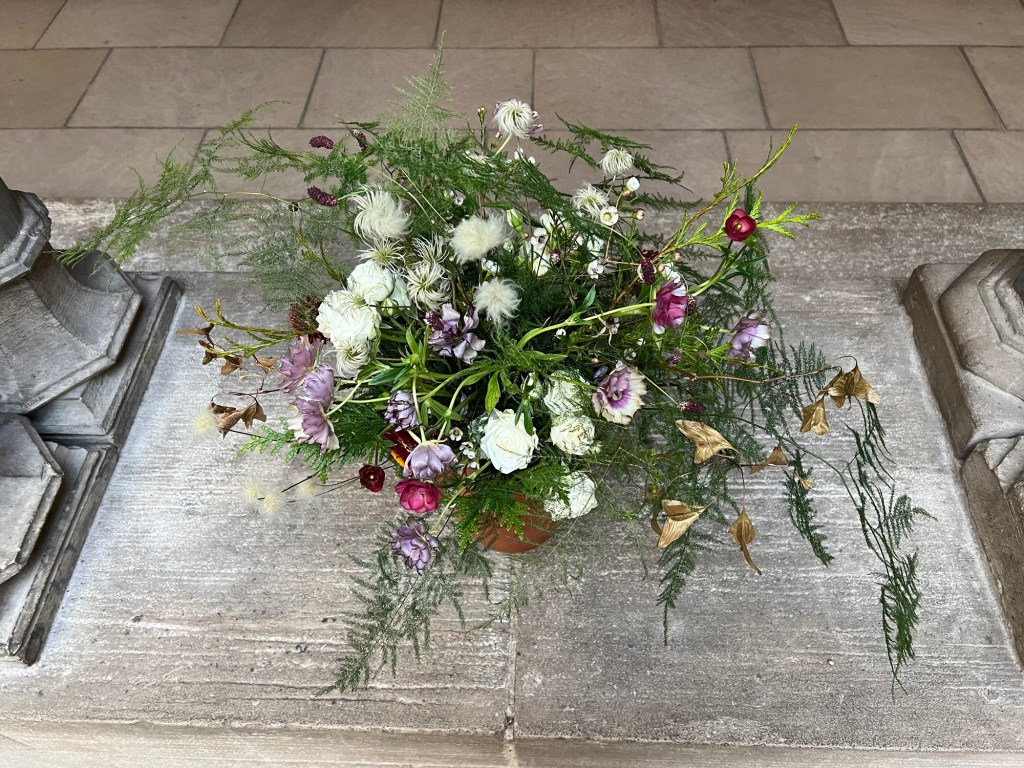
This led to a discussion about what each plant, flower and fruit meant in the Christian tradition, a clever way to justify decorating and celebrating during the holidays. Ivies, pine, winter flowers and even late season apples not only lined places of worship but gave a festive look and district smell to these buildings. A symbol of life in the cold winter months while they waited for the arrival of Spring.
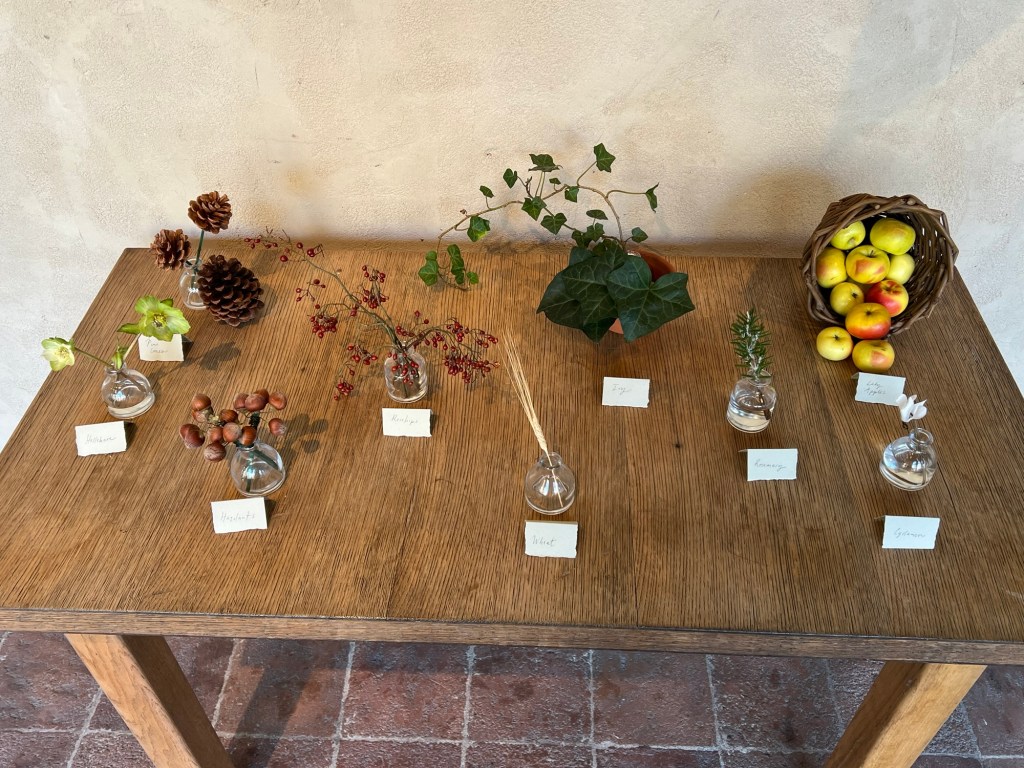

The plant types that decorated the houses of worship
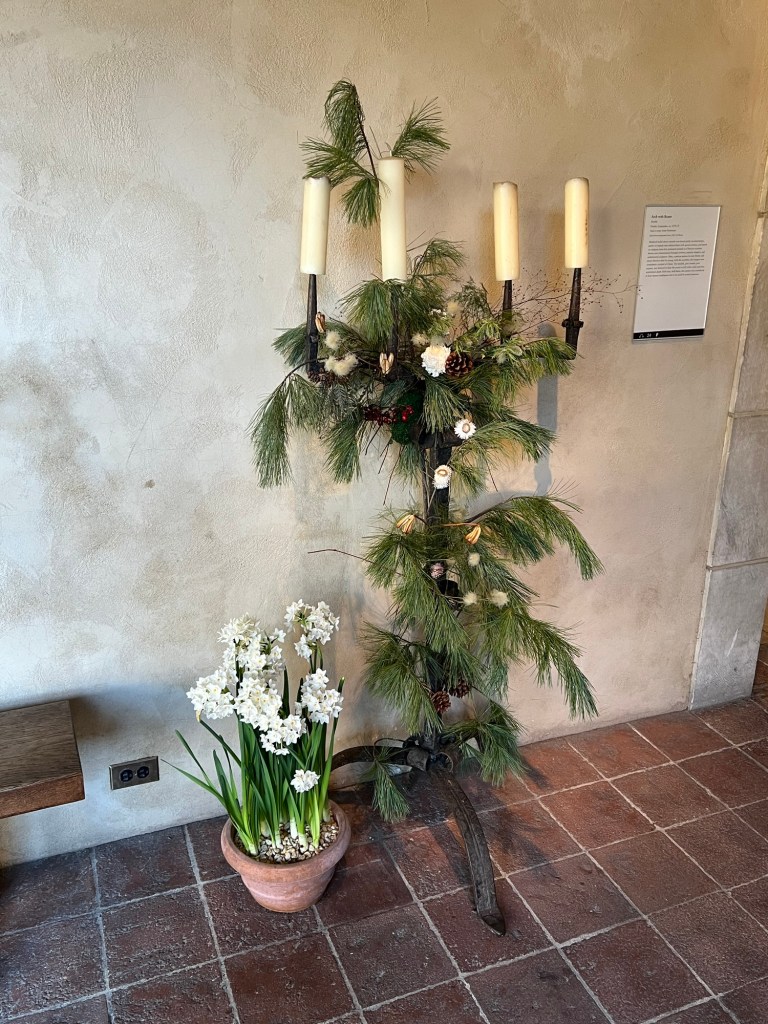

The flowers and plants lining the chapel
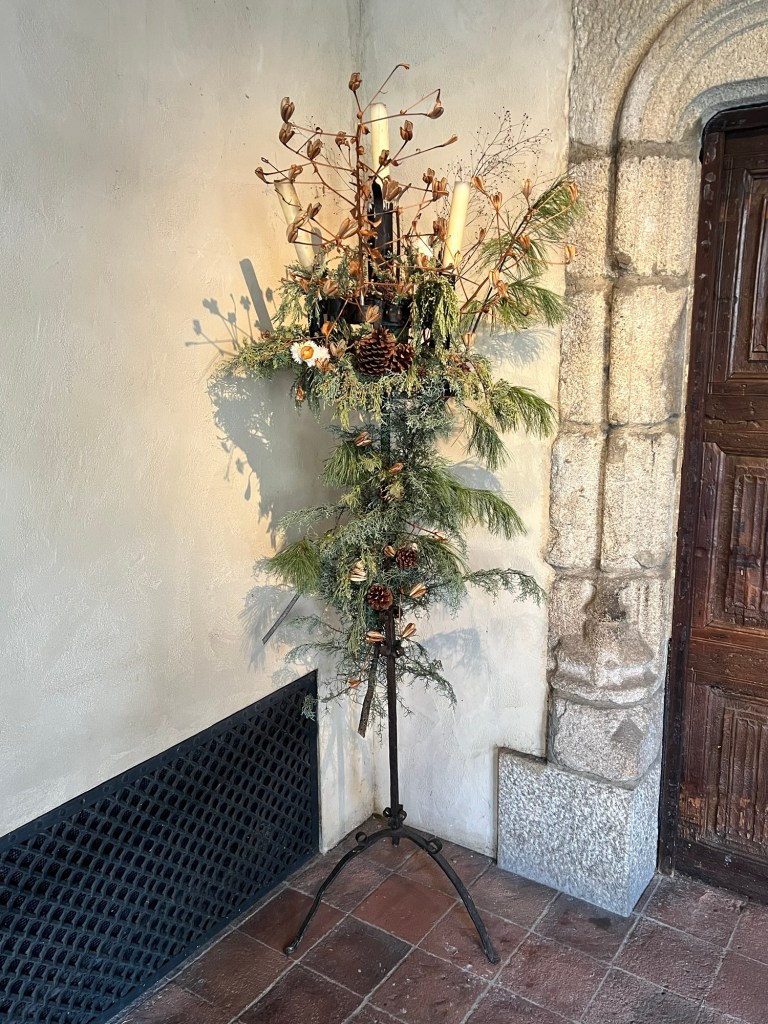

The decorative candle stands lining the walls of the chapel
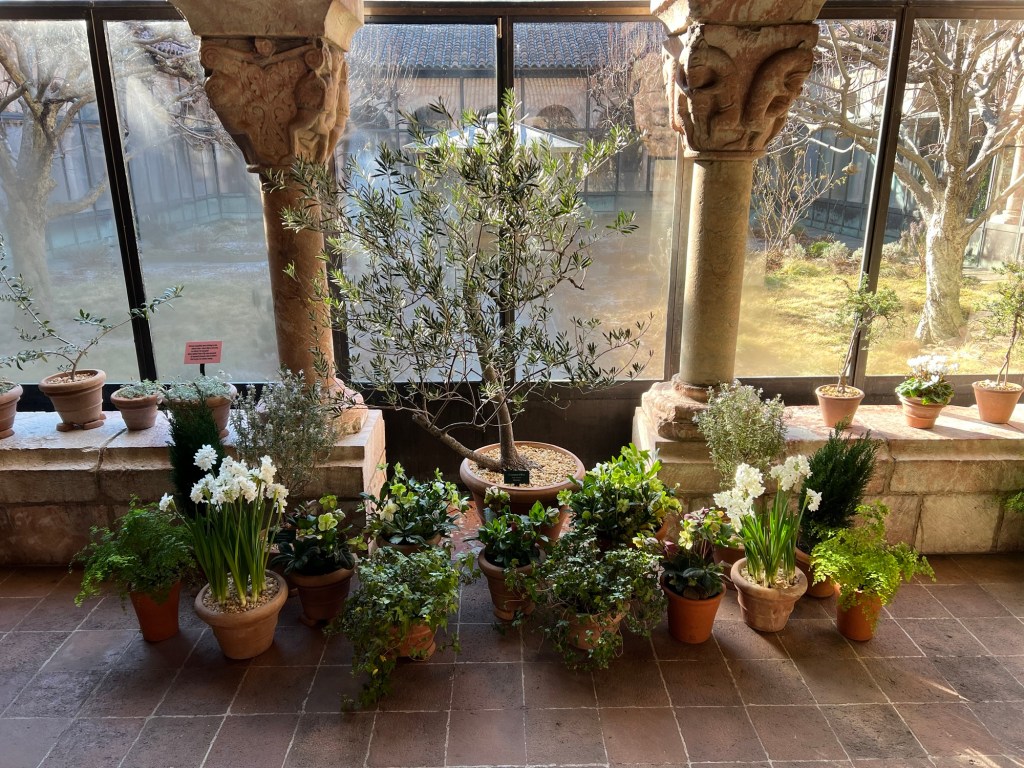
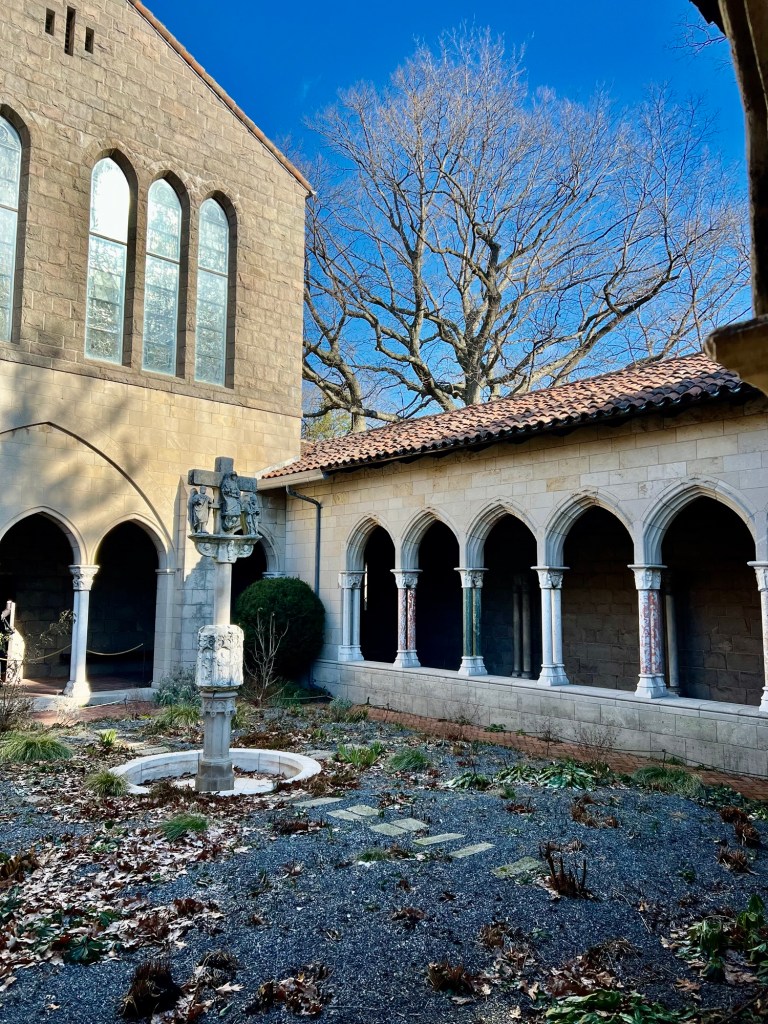
We then toured the main Cloister, closed for the Winter but was lined with plants, flowers and greens brighting every corner of the building. These were examples of plants and flowers that would have decorated these halls at the holidays.
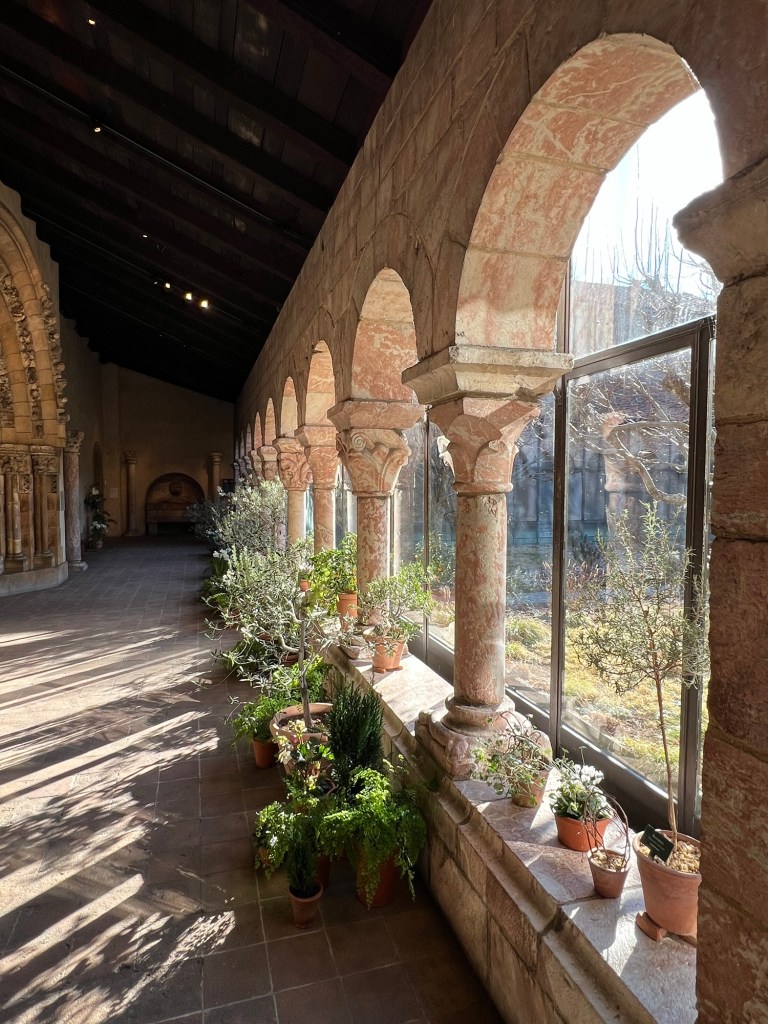

Walking the halls of the Cloisters

Touring the halls of the Cloisters with flowers and plants to celebrate the season
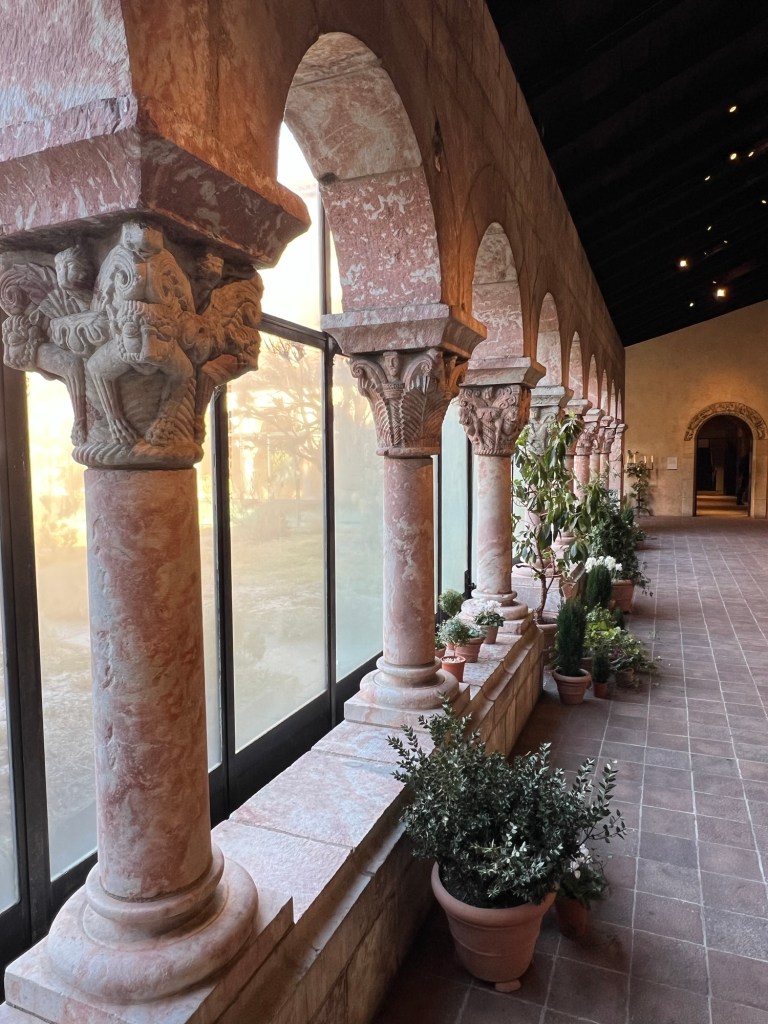

Walking the halls of the Cloisters
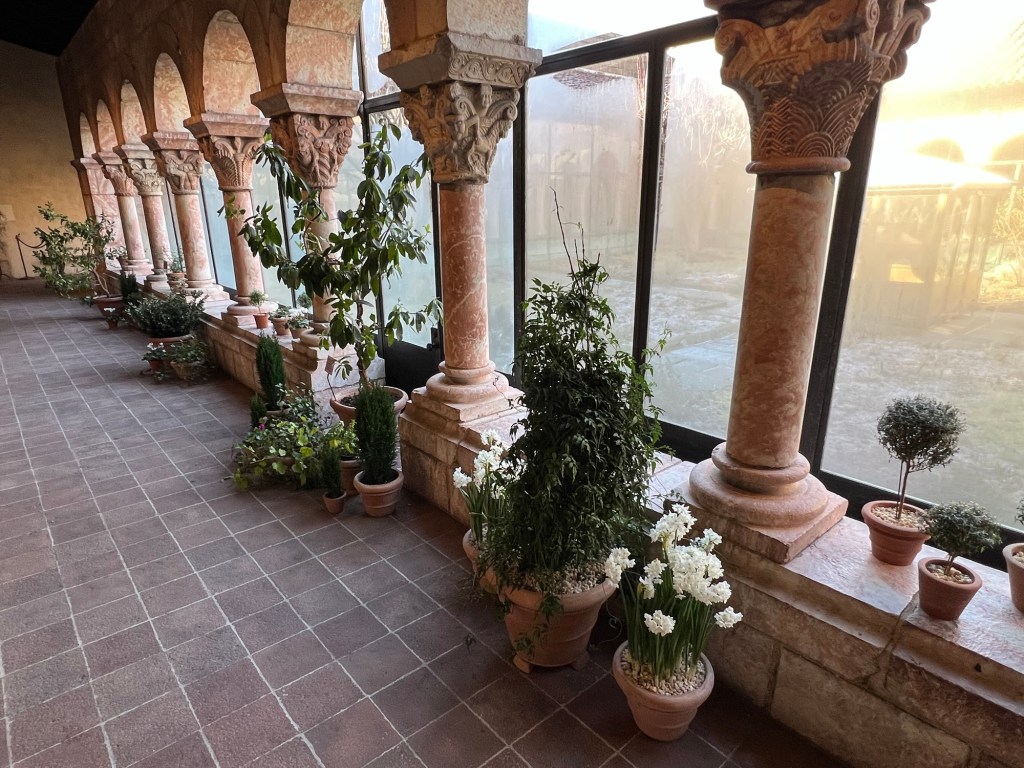

The flowering plants of the Cloisters
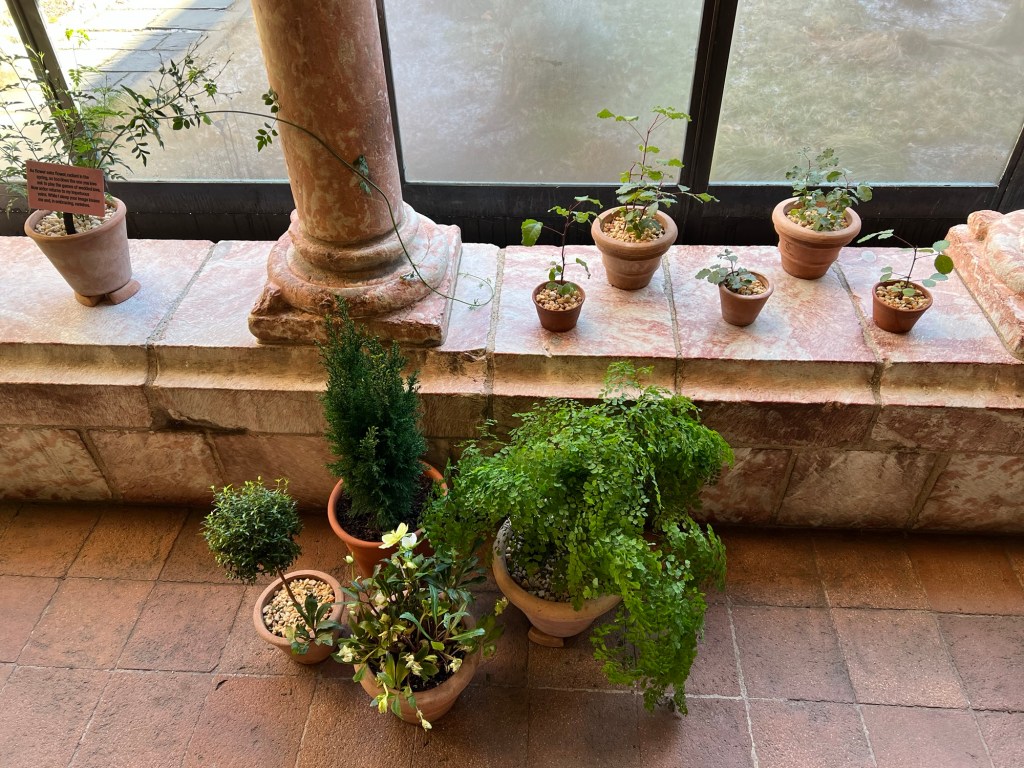

The flowering plants and vines that would have decorated churches in Medieval times
We then toured the Tapestry Room and discussed the use of plants in art form and the use of the detail as symbolism in art. These tapestries were meant to cover the drafty walls of palaces and bring in color and decoration to the stone walls.
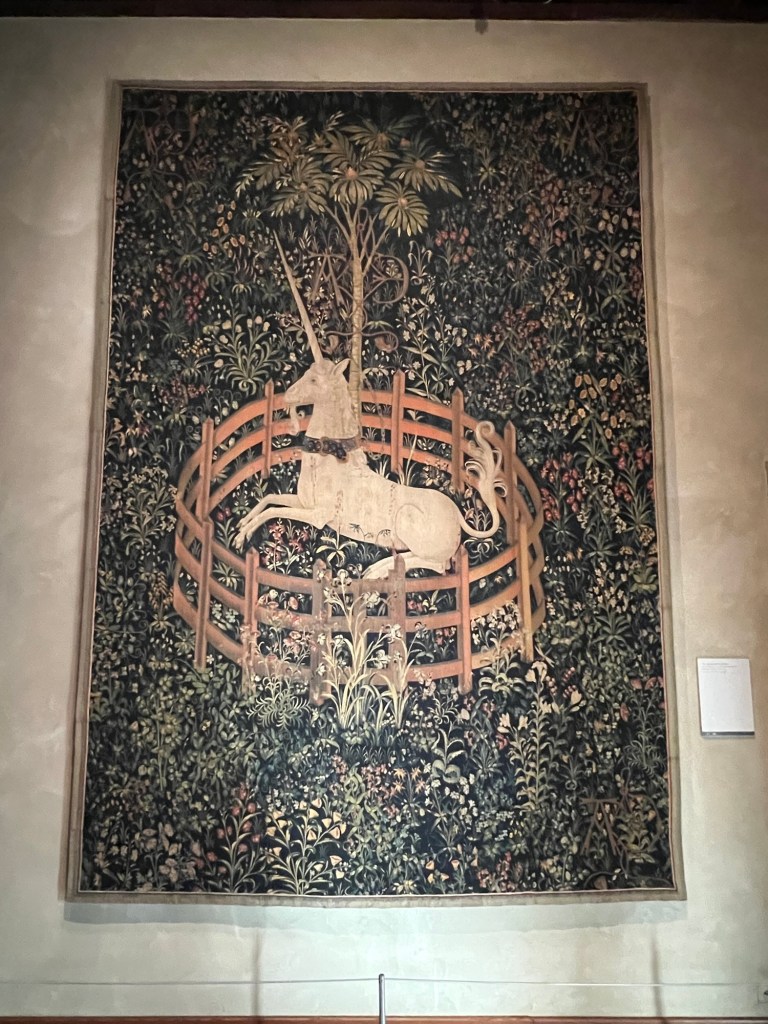

The famous ‘Hunt of the Unicorn’ tapestry
We then took a detour to the outside gardens that are enjoying their winter slumber. These gardens were used by the cloisters for food, medicines and decorative use. They will start coming to life in a few months.

The Cloisters Gardens
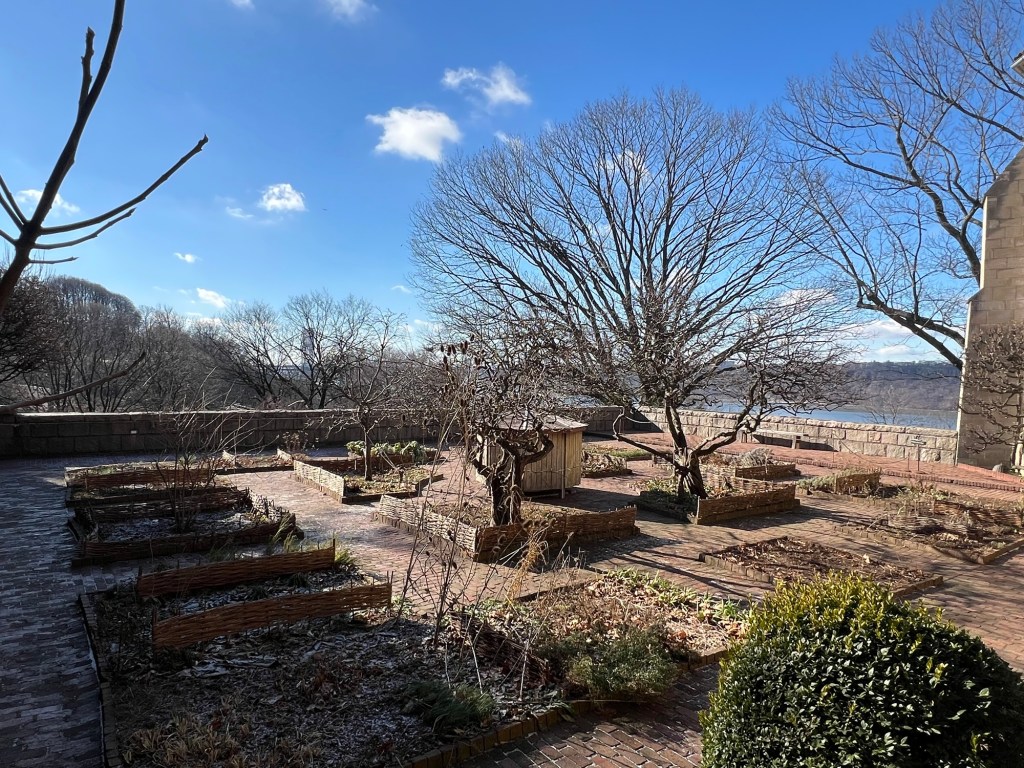

The garden terrace over looking the Hudson River
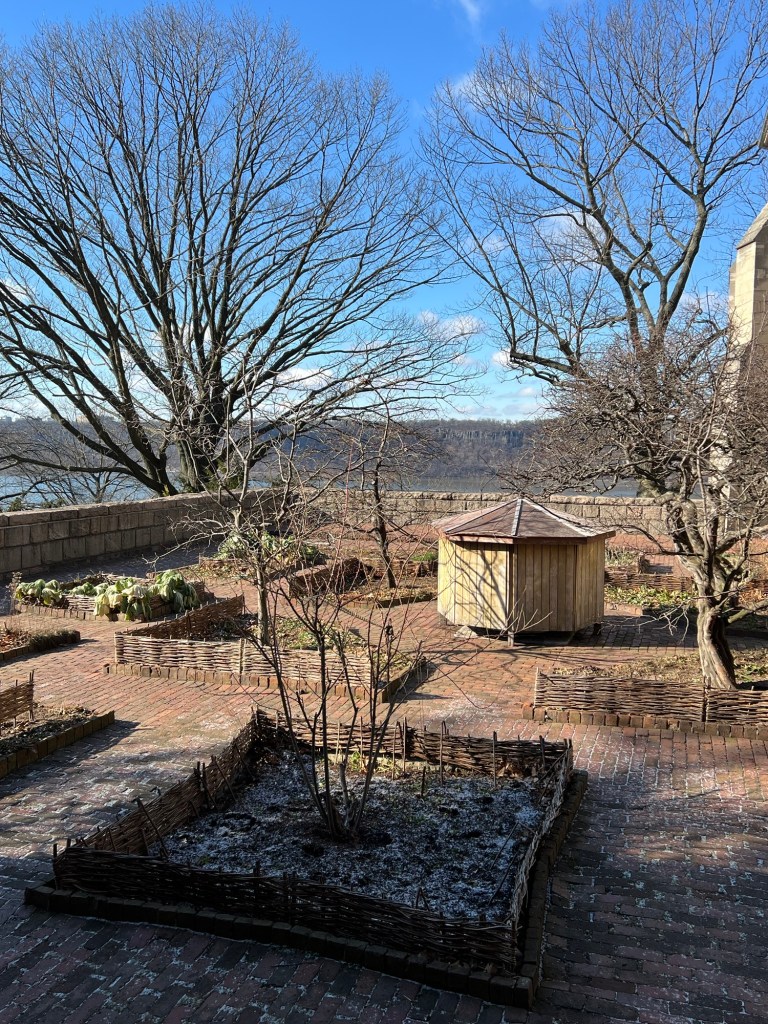

The terrace gardens in the winter waiting to come to life
Then we went back inside for a discussion of the Three Kings and the Epiphany and its symbolism in art at the Cloisters. These are some of the works featured on the ‘Christmas Tide’ tour to symbolize that visit.
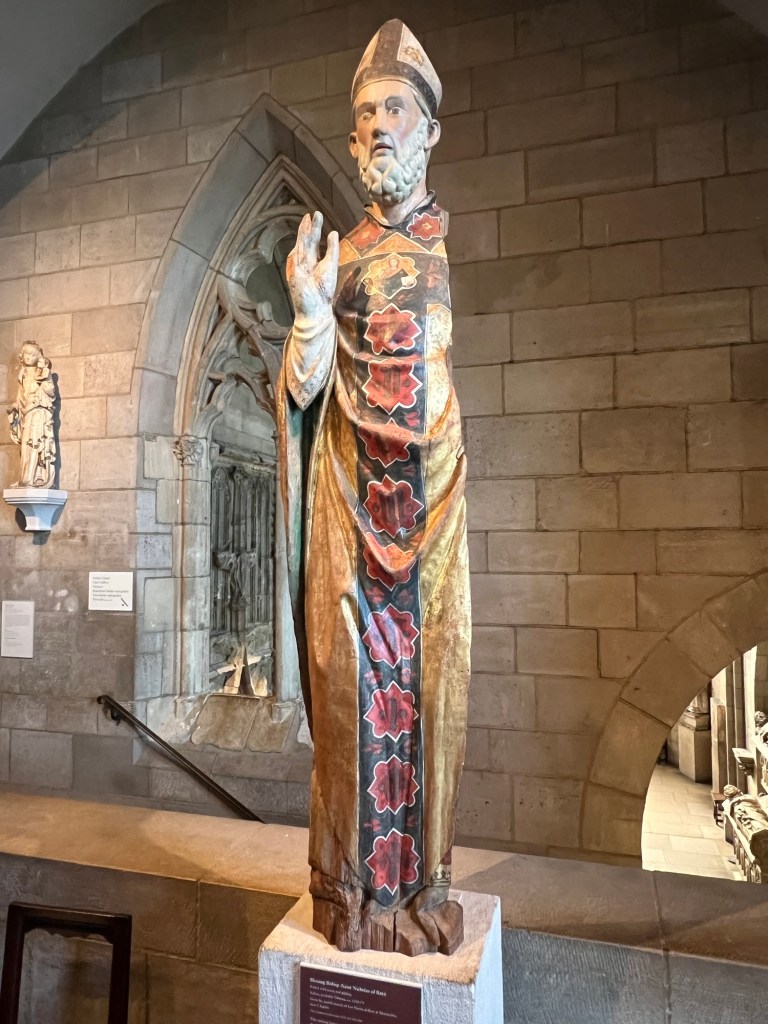

Some of the woodwork from that era
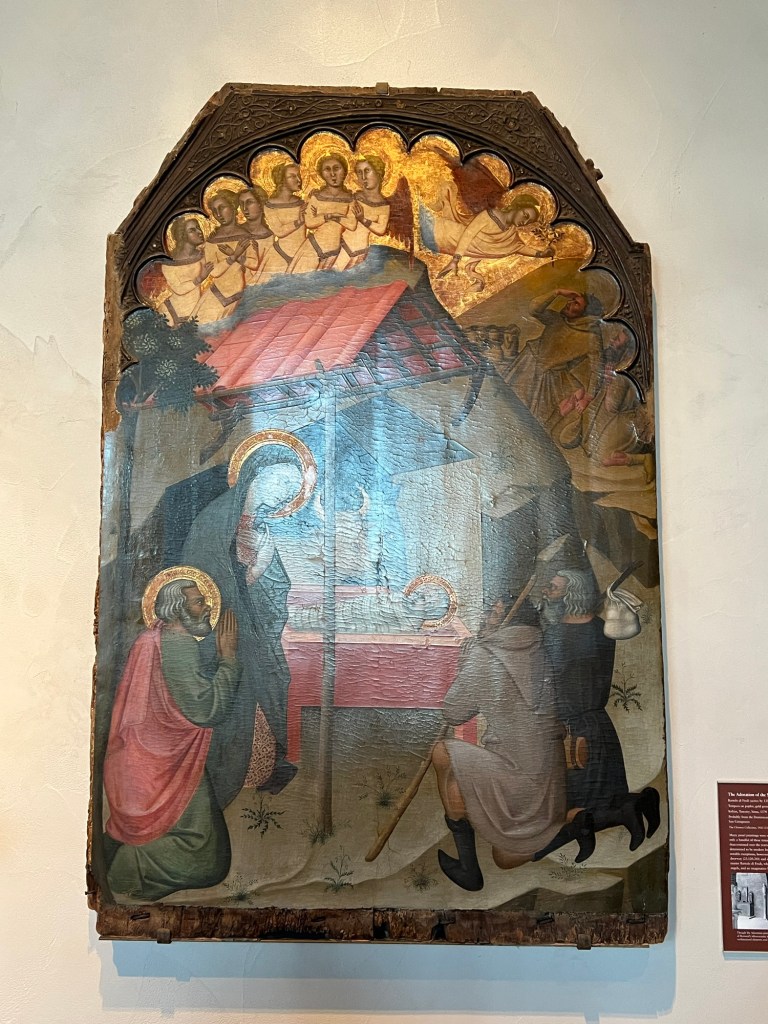

The Visitation of the Three Kings
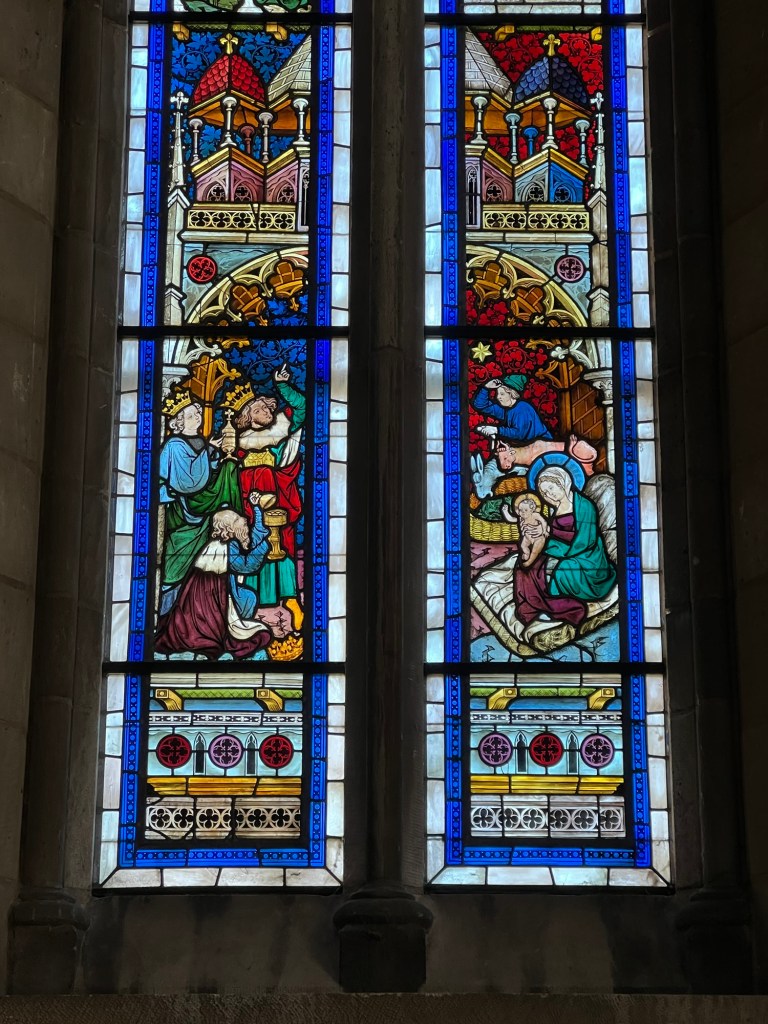

The Visitation of the Three Kings depicted in stained glass
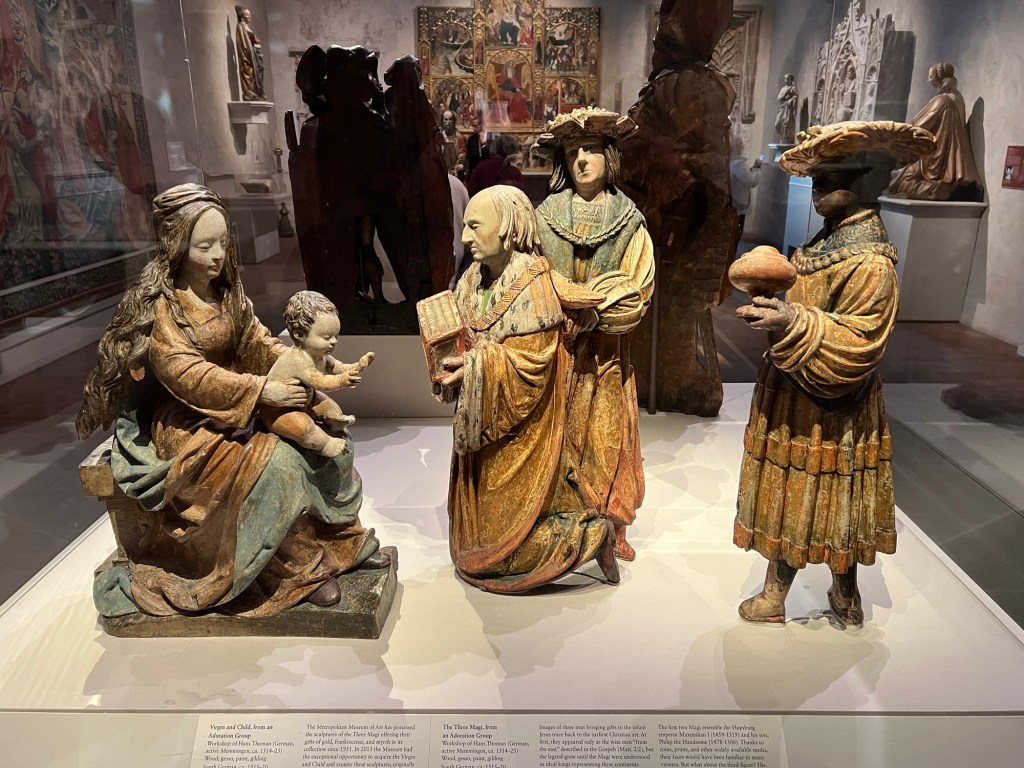

The Visitation of the Three Kings depicted in statuary
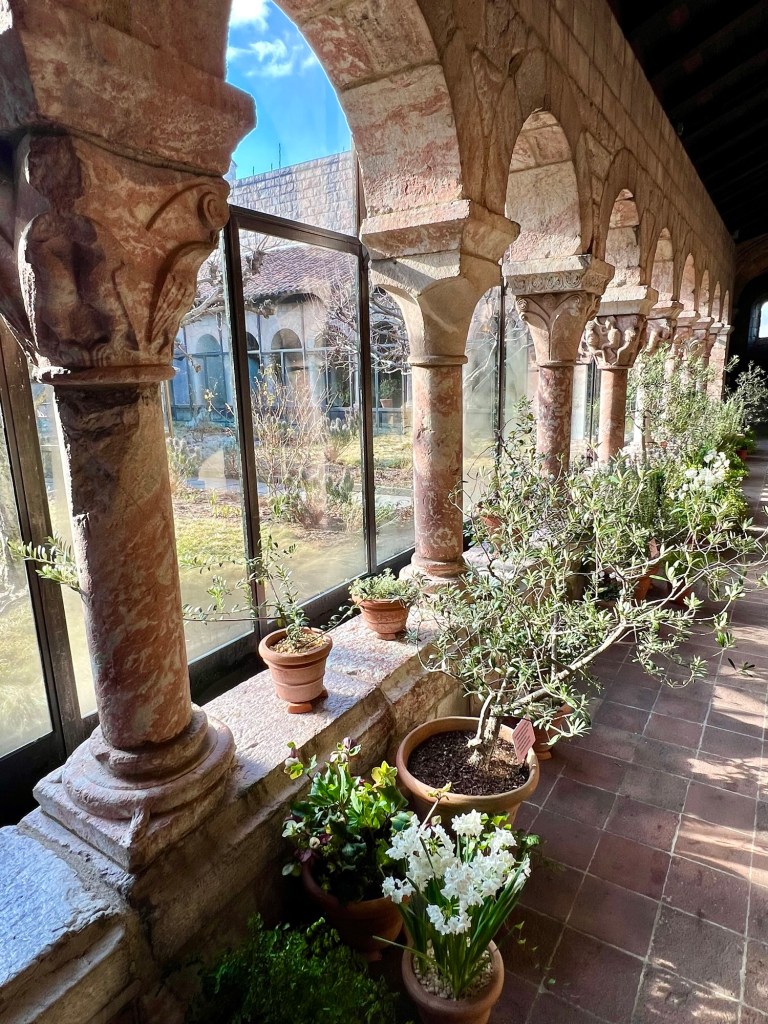

We visited the last of the Cloisters and discussed some of the plants in the collection
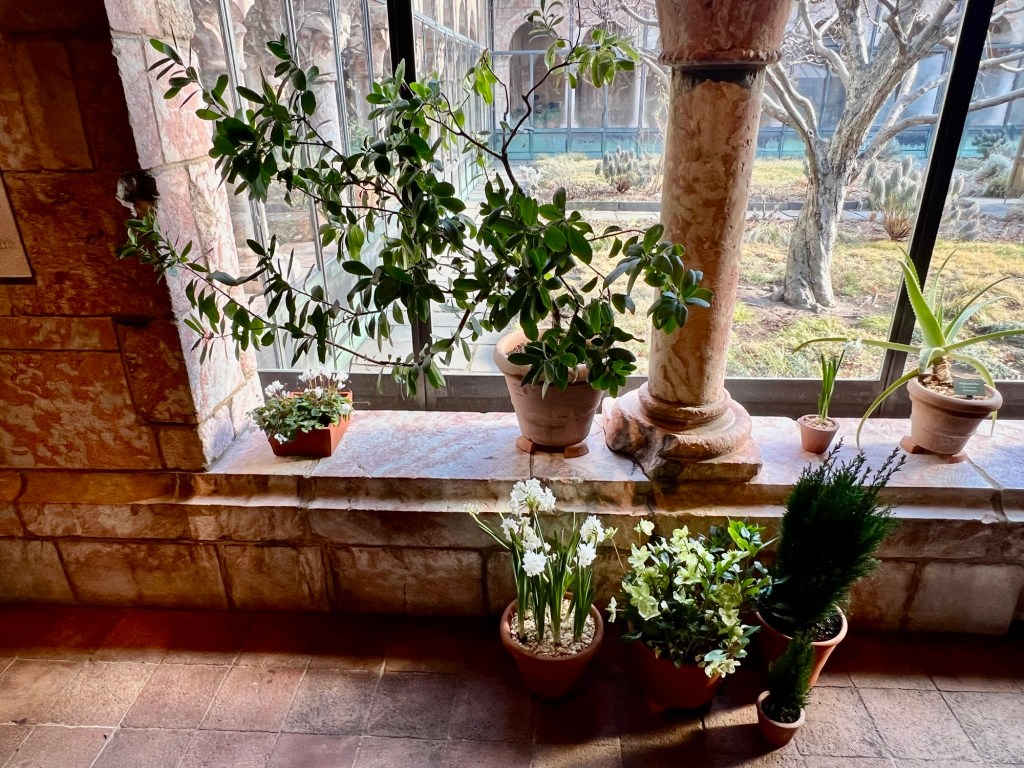

We were admiring the plants and flowers
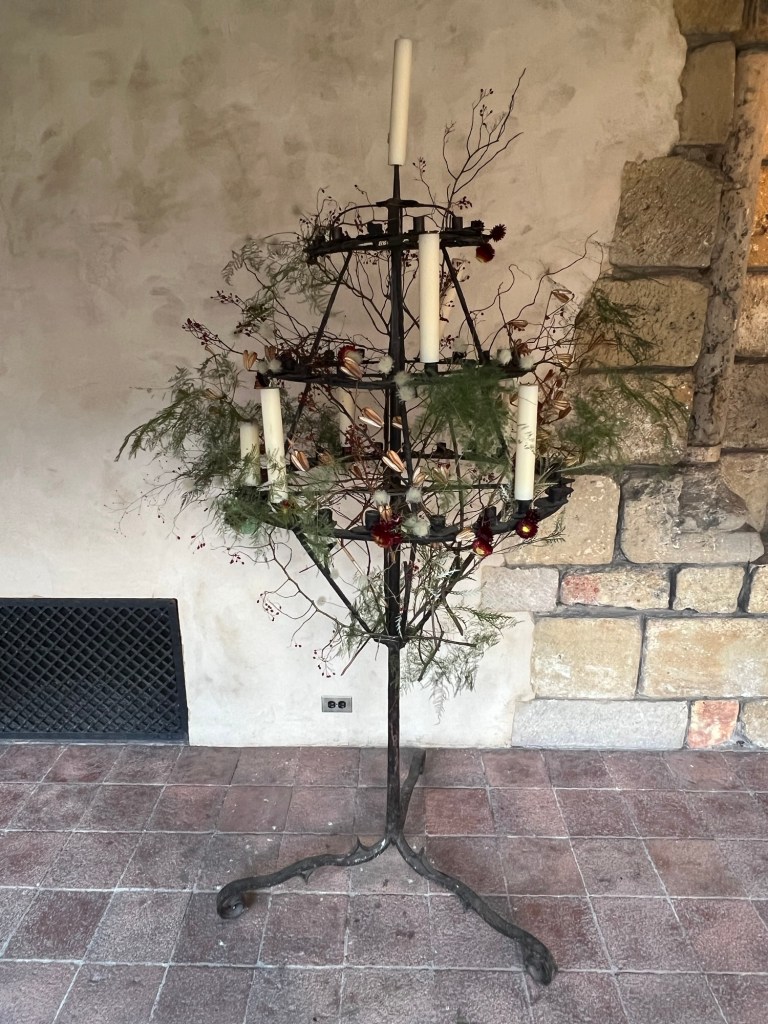
A candelabra in the hallway of the Cloisters
As I exited the building that afternoon, there were potted plants at the entrance of the Cloisters. It was a real treat to walk around the building at the holidays.

The potted plants outside the entrance of the museum
On my way down the stairs and out the door to Fort Tryon Park, I took another walk down the stone steps and walked through Ann Loftus Park. This popular playground was quiet this time of year, awaiting the Spring and the wonderful warm afternoons ahead.
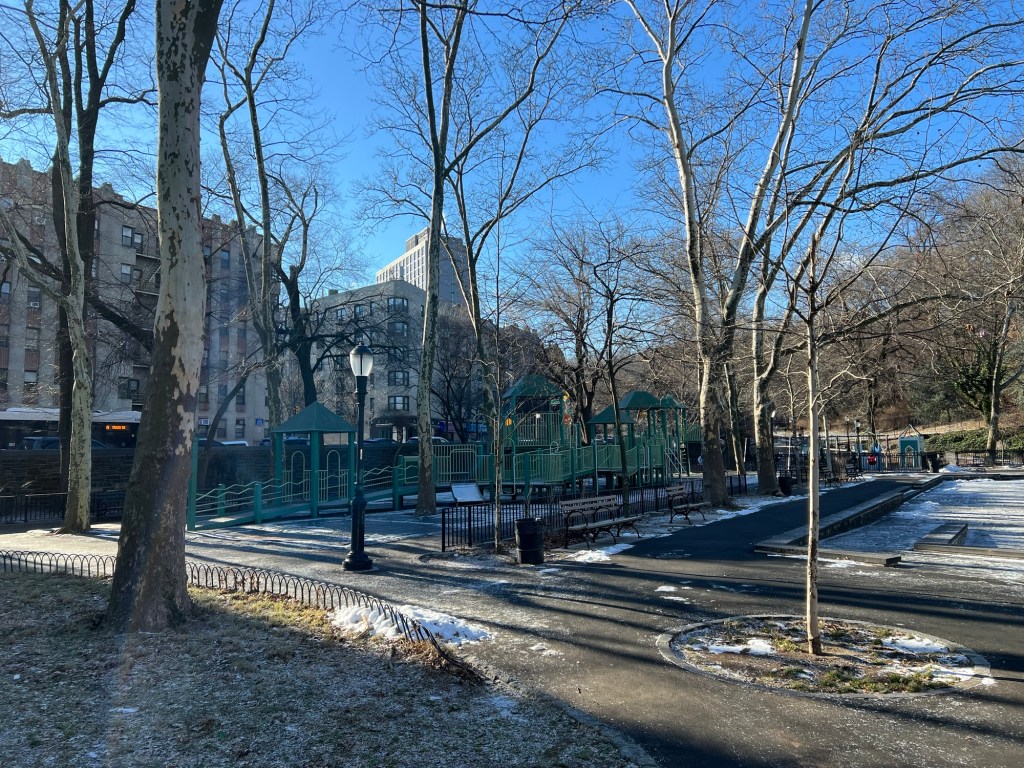

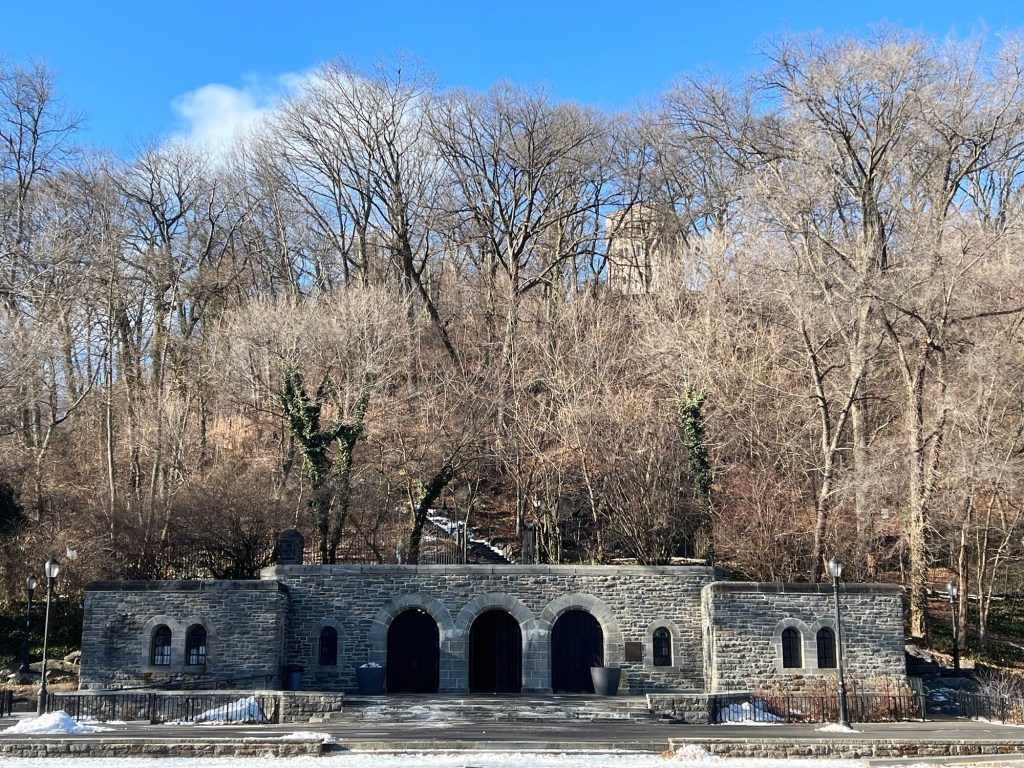
Walking through Fort Tryon Park
Fort Tyron Park
Riverside Drive to Broadway
New York, NY 10040
https://www.nycgovparks.org/parks/fort-tryon-park
https://www.nycgovparks.org/parks/fort-tryon-park/history
Open: Sunday-Saturday 6:00am-1:00am
My review on TripAdvisor:
My review on VisitingaMuseum.com:
https://visitingamuseum.com/tag/fort-tyron-park/

Ann Loftus Park in the winter time
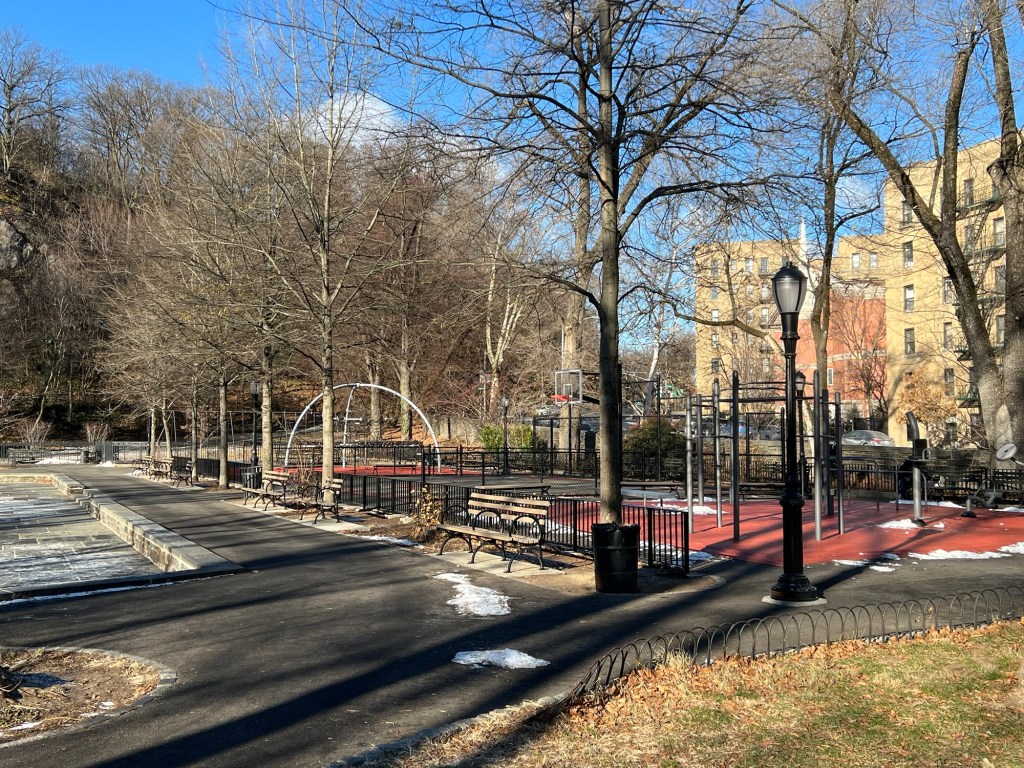

Ann Loftus Park quiet in the winter

Ann Loftus Park upon leaving the park that afternoon. The quiet beauty of the Winter.
https://www.nycgovparks.org/parks/fort-tryon-park/highlights/11234
https://www.nycgovparks.org/facilities/playgrounds/325
After the tour was over, I went to G’s Coffee Shop for second breakfast that morning.

G’s Coffee Shop at 634 West 207th Street
G’s Coffee Shop
634 West 207th Street
New York, NY 10034
(212) 942-0679
Free Delivery
Open: Sunday-Saturday 7:00am-9:00pm
https://www.facebook.com/pages/category/Breakfast—Brunch-Restaurant/Gs-Coffee-Shop-205601462950934/
My review on TripAdvisor:
My review on DiningonaShoeStringinNYC@Wordpress.com:
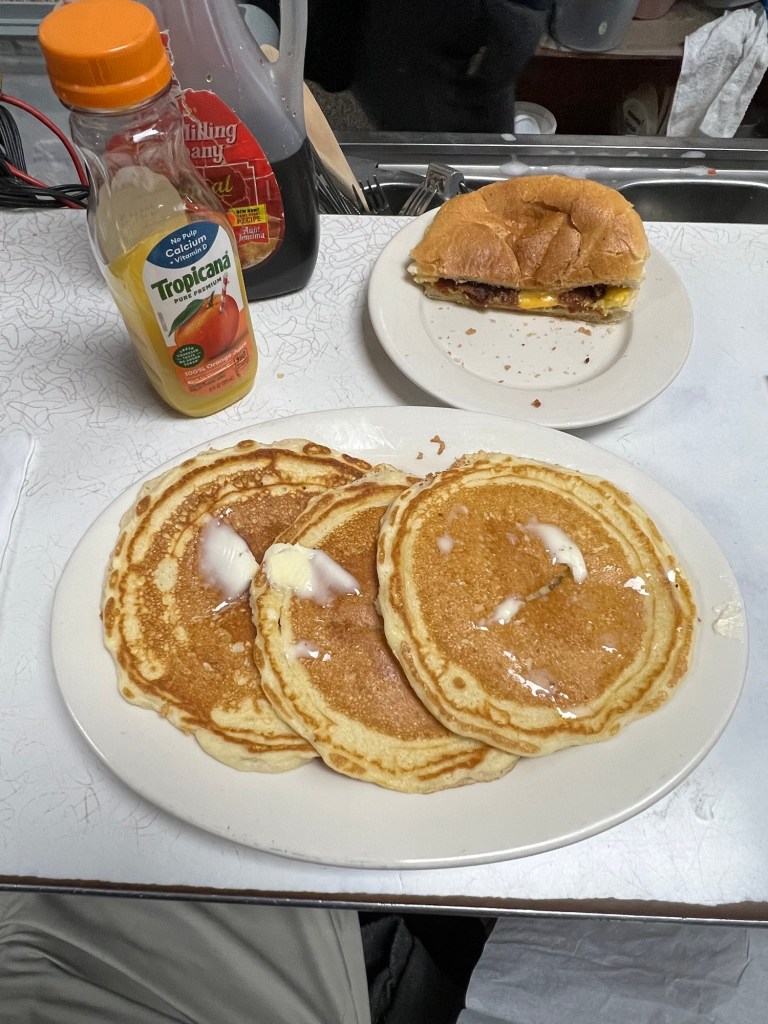

My breakfast at G’s Coffee Shop
I love coming for breakfast at G’s Coffee Shop after a tour of The Cloisters. The food and service of this small ‘hole in the wall’ diner is wonderful. The meals are so reasonable and when you dine at the counter, you can watch the food cooked right in front of you. I had a wonderful Bacon, Egg and Cheese sandwich with a side of golden pancakes. What a great meal on a cold winter morning.

The Bacon, Egg and Cheese sandwich

The breakfast sandwiches here are so good

The pancakes were wonderful. The perfect comfort food on a winter day.
It was a really great tour and it was fun to walk around the neighborhood through the parks and seeing all the post Christmas decorations. Inwood is a really beautiful section of Manhattan with lots to do and see. It is the perfect place to spend the Christmas break.