Stony Point Battlefield State Historic Park
44 Battlefield Road
Stony Point, NY 10980
(845) 786-2521
https://parks.ny.gov/historic-sites/stonypointbattlefield/maps.aspx
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stony_Point_Battlefield
Open: Sunday (Grounds) 12:00pm-5:00pm (Museum) 12:00pm-4:30pm /Monday-Tuesday Closed/Wednesday-Saturday (Grounds) 9:00am-5:00pm/(Museum) 10:00am-4:30pm
Admission: Free but donations are accepted. Groups, Scouts and Organizations are $5.00 individuals per person and $7.00 for special events per person. Please call to make arrangements on this.
My review on TripAdvisor:

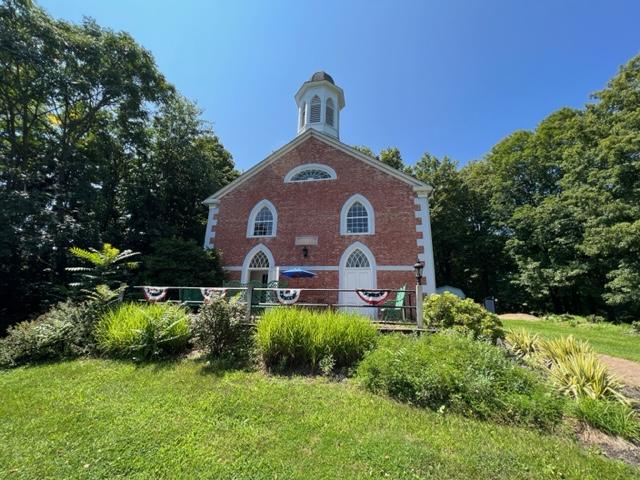
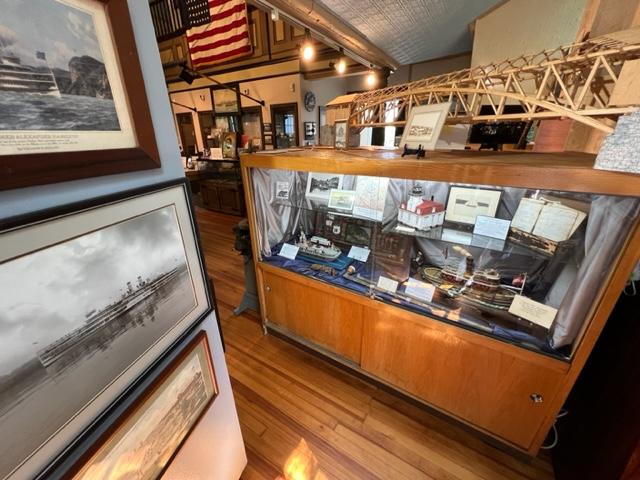
The Stony Point Battlefield Museum

The General’s tent on the battlefield.
We visited the Stony Point Battlefield one afternoon and it is a very interesting and historical fort in the Hudson River Valley. We were able to tour the battle site and explore the grounds of this historical site. Then we toured the museum which gave us a view of the battle and what happened that night through a series of displays of the artifacts.

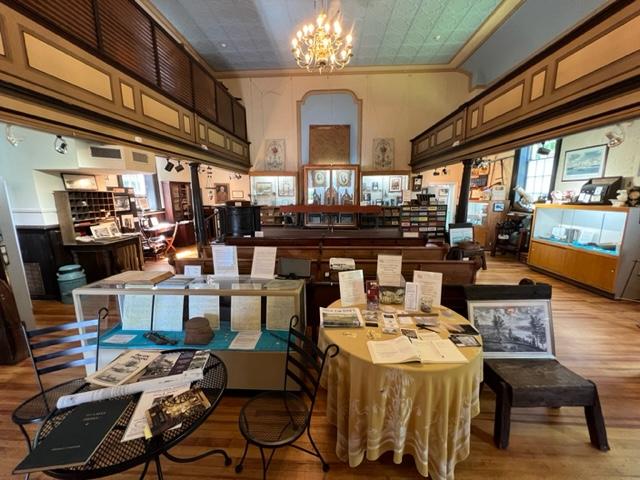
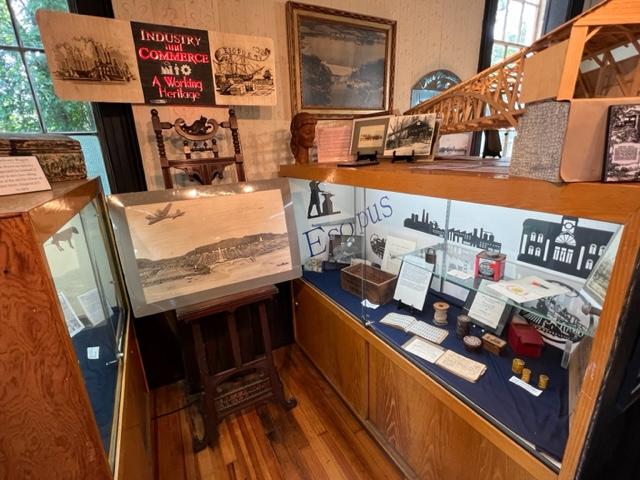
The Gallery

The Gallery
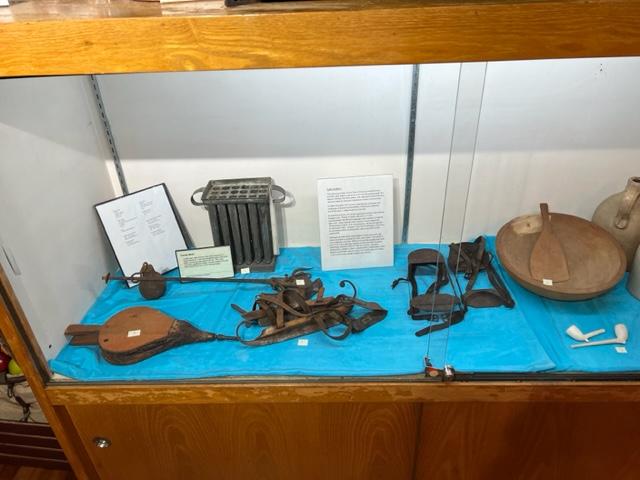
The gallery was filled with all sorts of weaponry and items needed by the troops for battle.

The battlefield site.
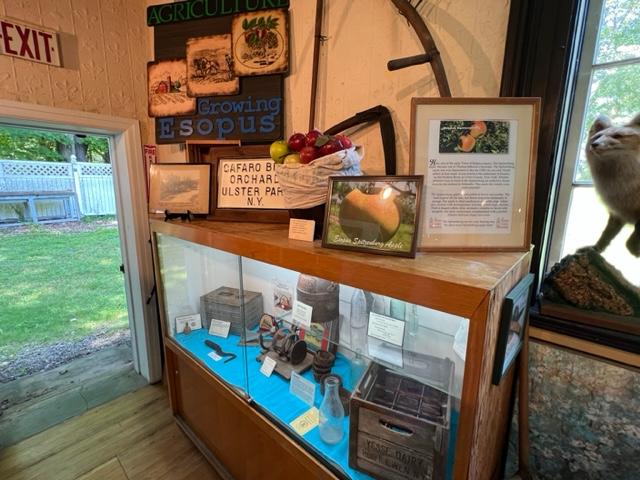
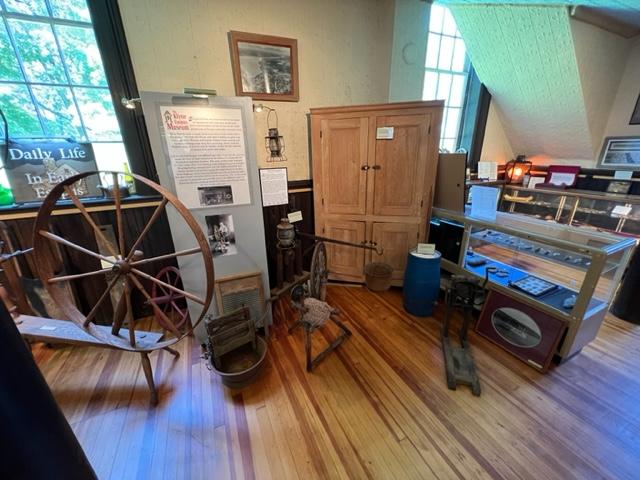
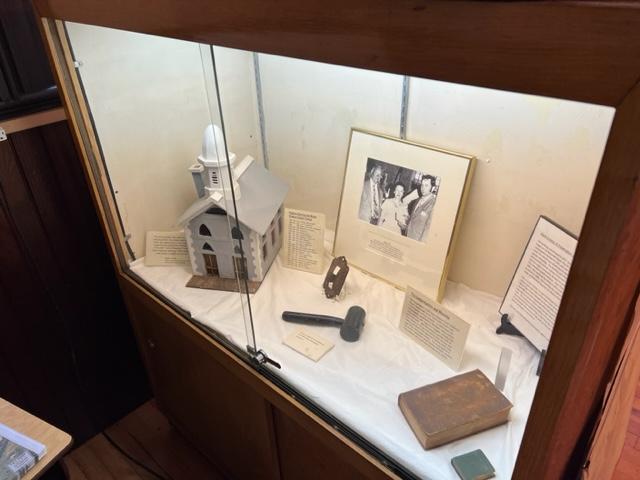
The museum has displays of the weapons used, the structure of the fort, utensils used the time that the troops were defending this area and what life was like on a day-to-day basis. The museum also offers a glimpse of artifacts of both the fort and of the battle with docents assisting you in telling the story of what happened at that time and after the battle and the war were over.

The Stoney Point Battlefield tent set up.
Outside the fort, there was a set-up of tents to show what the troops life was like in battle as well as General Wallace’s tent that he lived in and used during the battle. At the end of the day, the park does a demonstration of lighting the cannon that would have been used in battle. That was interesting. It was a lot more work than people think.

The cannon set up.
There is lot to do and see along the pathways of the fort and its grounds with amazing views of the Hudson River.

The story of the battle.
The History of the park and battlegrounds:
(from the NYS Parks Division website)
Visit the site of the Battle of Stony Point, one of the last Revolutionary War battles in the northeastern colonies. This is where Brigadier General Anthony Wayne led his corps of Continental Light Infantry in a daring midnight attack on the British, seizing the site’s fortifications and taking the soldiers and camp followers at the British garrison as prisoners on July 16, 1779.

The map of the fort at Stony Point, NY.
By May 1779 the war had been raging for four years and both sides were eager for a conclusion. Sir Henry Clinton, Commander-In-Chief of the British forces in America, attempted to coerce General George Washington into one decisive battle to control the Hudson River. As part of his strategy, Clinton fortified Stony Point. Washington devised a plan for Wayne to lead an attack on the garrison. Armed with bayonets only, the infantry captured the fort in short order, ending British control of the river.

The weapons of battle on display at the museum.
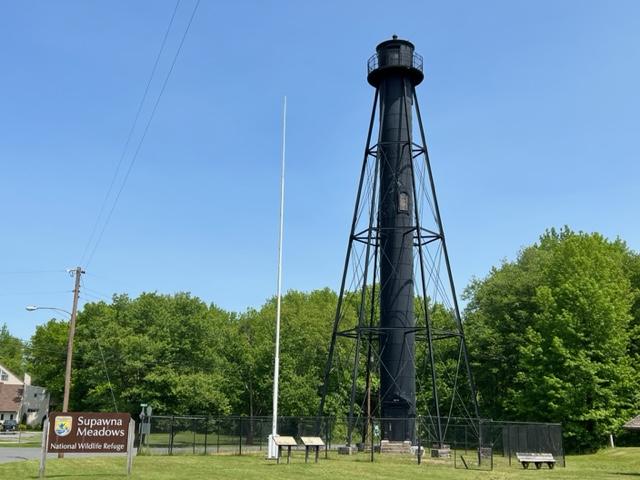
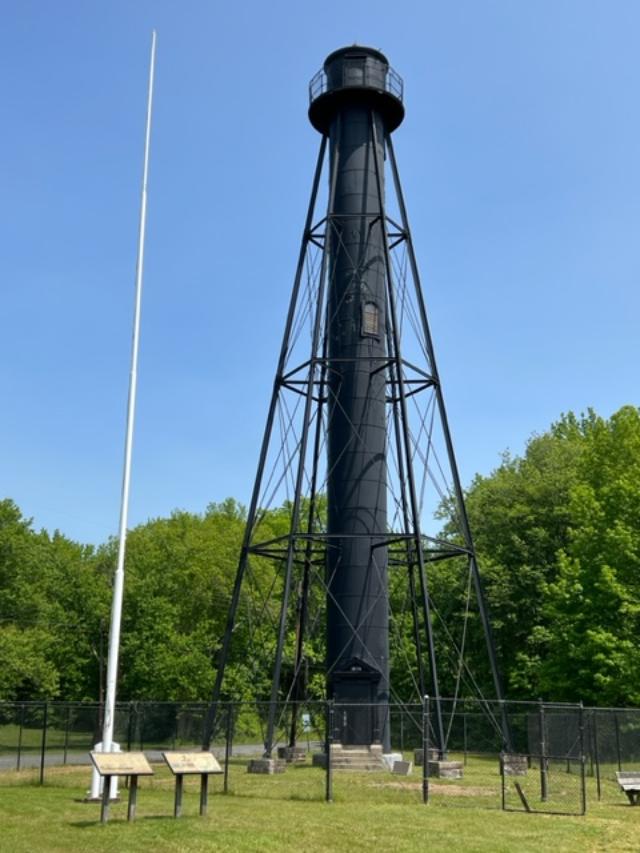
The Stony Point Lighthouse, built in 1826, is the oldest lighthouse on the Hudson River. De-commissioned in 1925, it now stands as a historical reminder of the importance of lighthouses to commerce on the Hudson River. The opening of the Erie Canal in 1825 unleashed a surge of commercial navigation along the Hudson River, by linking New York city to America’s heartland.
Within a year, the first of the Hudson’s fourteen lights shone at Stony Point and others soon followed, designed to safely guide maritime travel along the river. Many light keepers, including several remarkable women such as Nancy and Melinda Rose at Stony Point, made their homes in the lighthouse complexes, and ensured that these important navigational signals never failed to shine.
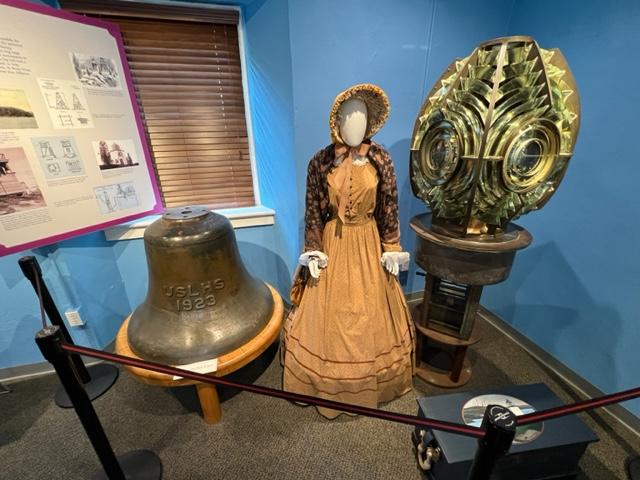

The lighthouse light on display at the museum.
The site features a museum, which offers exhibits on the battle and the Stony Point Lighthouse, as well as interpretive programs, such as reenactments highlighting 18th century military life, cannon and musket firings, cooking demonstrations, and children’s activities and blacksmith demonstrations.

The cannon demonstration that we saw at the end of our visit to the battlefields.